doc: Refactor documentation
This commit is contained in:
parent
91a4c68e06
commit
1b254234c7
1
.gitignore
vendored
1
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
.env
|
||||
.idea
|
||||
docker-compose.override.yml
|
||||
/heimdall
|
||||
!/heimdall/.gitkeep
|
||||
/sonarr
|
||||
|
||||
173
CONFIGURATION.md
173
CONFIGURATION.md
@ -1,173 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
`cp .env.example .env`
|
||||
|
||||
then fill the `.env` file with your variables:
|
||||
|
||||
- `USER_ID`: ID of the user to use in Docker containers, defaults to `1000`
|
||||
- `GROUP_ID`: ID of the user group to use in Docker containers, defaults to `1000`
|
||||
- `TIMEZONE`: for the containers, defaults to `America/New_York`
|
||||
- `DATA_ROOT`: host location of the data files, defaults to `/mnt/data`
|
||||
- `DOWNLOAD_ROOT`: host download location for qBittorrent, should be a subfolder of `DATA_ROOT`, defaults to `/mnt/data/torrents`
|
||||
- `PIA_LOCATION`: servers to use for PIA, defaults to `ca`, ie Montreal, Canada with port forwarding support
|
||||
- `PIA_USER`: PIA username
|
||||
- `PIA_PASS`: PIA password
|
||||
- `PIA_LOCAL_NETWORK`: PIA local network
|
||||
|
||||
## PIA Wireguard VPN
|
||||
|
||||
I chose PIA since it supports Wireguard and [port forwarding](https://github.com/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia/issues/26#issuecomment-868165281),
|
||||
but you could use other providers:
|
||||
|
||||
- OpenVPN: [linuxserver/openvpn-as](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/openvpn-as)
|
||||
- Wireguard: [linuxserver/wireguard](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/wireguard)
|
||||
- NordVPN + OpenVPN: [bubuntux/nordvpn](https://hub.docker.com/r/bubuntux/nordvpn/dockerfile)
|
||||
- NordVPN + Wireguard (NordLynx): [bubuntux/nordlynx](https://hub.docker.com/r/bubuntux/nordlynx)
|
||||
|
||||
For PIA + Wireguard, fill `.env` and fill it with your PIA credentials.
|
||||
|
||||
The location of the server it will connect to is set by `LOC=ca`, defaulting to Montreal - Canada.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sonarr & Radarr
|
||||
|
||||
### File Structure
|
||||
|
||||
Sonarr and Radarr must be configured to support hardlinks, to allow instant moves and prevent using twice the storage
|
||||
(Bittorrent downloads and final file). The trick is to use a single volume shared by the Bittorrent client and the *arrs.
|
||||
Subfolders are used to separate the TV shows from the movies.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration is well explained by [this guide](https://trash-guides.info/Hardlinks/How-to-setup-for/Docker/).
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, the final structure of the shared volume will be as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
data
|
||||
├── torrents = shared folder qBittorrent downloads
|
||||
│ ├── movies = movies downloads tagged by Radarr
|
||||
│ └── tv = movies downloads tagged by Sonarr
|
||||
└── media = shared folder for Sonarr and Radarr files
|
||||
├── movies = Radarr
|
||||
└── tv = Sonarr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go to Settings > Management.
|
||||
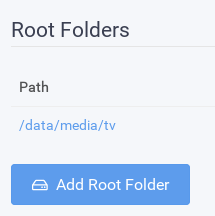
In Sonarr, set the Root folder to `/data/media/tv`.
|
||||
In Radar, set the Root folder to `/data/media/movies`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Client
|
||||
|
||||
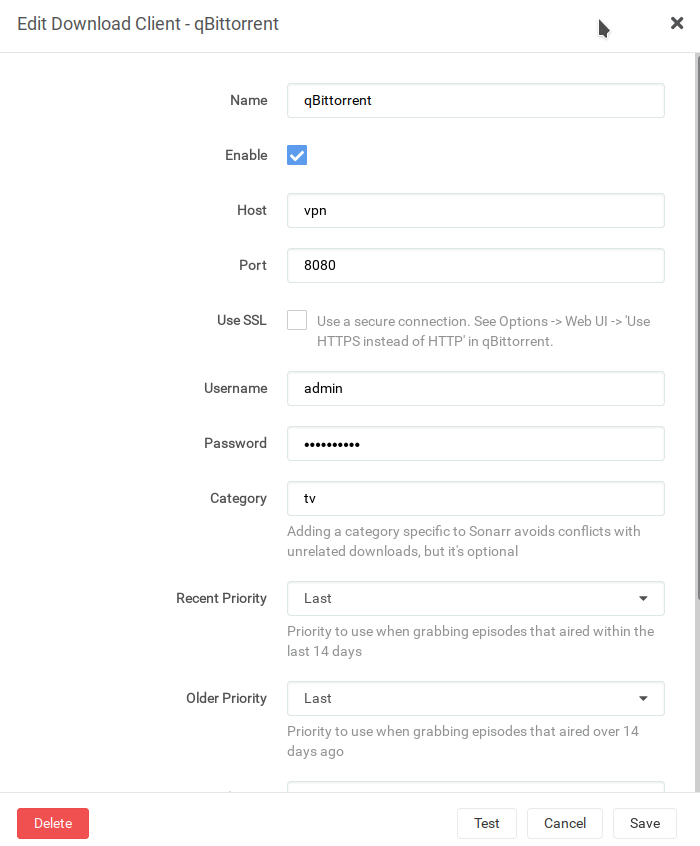
Then qBittorrent can be configured at Settings > Download Clients. Because all the networking for qBittorrent takes
|
||||
place in the VPN container, the hostname for qBittorrent is the hostname of the VPN container, ie `vpn`, and the port is `8080`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Prowlarr
|
||||
|
||||
The indexers are configured through Prowlarr. They synchronize automatically to Radarr and Sonarr.
|
||||
|
||||
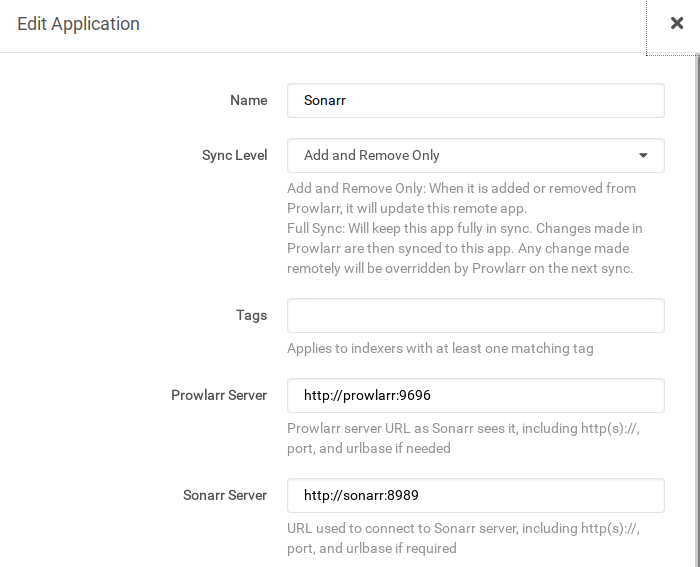
Radarr and Sonarr may then be added via Settings > Apps. The Prowlarr server is `http://prowlarr:9696/prowlarr`, the Radarr server
|
||||
is `http://radarr:7878/radarr` and Sonarr `http://sonarr:8989/sonarr`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Their API keys can be found in Settings > Security > API Key.
|
||||
|
||||
## qBittorrent
|
||||
|
||||
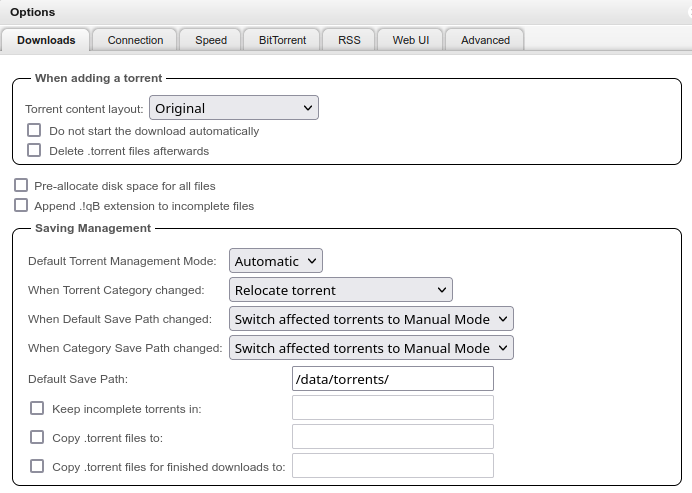
Set the default save path to `/data/torrents` in Settings:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
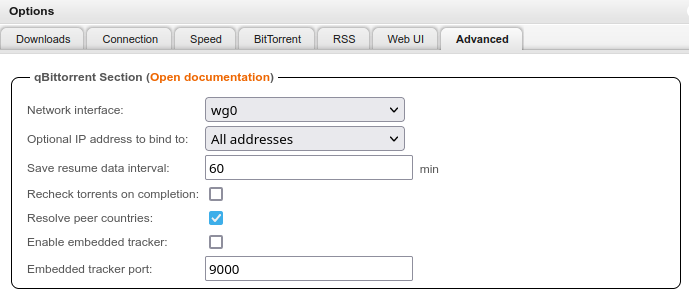
Restrict the network interface to Wireguard:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The web UI login page can be disabled on for the local network in Settings > Web UI > Bypass authentication for clients
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.0.0/16
|
||||
127.0.0.0/8
|
||||
172.17.0.0/16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Jellyfin
|
||||
|
||||
To enable [hardware transcoding](https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/administration/hardware-acceleration/),
|
||||
depending on your system, you may need to update the following block:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128
|
||||
- /dev/dri/card0:/dev/dri/card0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, running Docker on Linux you will want to use VA-API, but the exact mount paths may differ depending on your
|
||||
hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
## Heimdall
|
||||
|
||||
Applications can be added in Items > Add. The URLs should be the static IP, ie: `http://192.168.0.10/` for Sonarr
|
||||
for example.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Traefik and SSL Certificates
|
||||
|
||||
While you can use the private IP to access your NAS, how cool would it be for it to be accessible through a subdomain
|
||||
with a valid SSL certificate?
|
||||
|
||||
Traefik makes this trivial by using Let's Encrypt and one of its
|
||||
[supported ACME challenge providers](https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/acme/).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's assume we are using `nas.domain.com` as custom subdomain.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea is to create an A record pointing to the private IP of the NAS, `192.168.0.10` for example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
nas.domain.com. 1 IN A 192.168.0.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The record will be publicly exposed but not resolve given this is a private IP.
|
||||
|
||||
Given the NAS is not accessible from the internet, we need to do a dnsChallenge.
|
||||
Here we will be using CloudFlare, but the mechanism will be the same for all DNS providers
|
||||
baring environment variable changes, see the Traefik documentation above and [Lego's documentation](https://go-acme.github.io/lego/dns/).
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we need to fill the `.env` entries:
|
||||
|
||||
- `HOSTNAME`: the subdomain used, `nas.domain.com` for example
|
||||
- `LETS_ENCRYPT_EMAIL`: e-mail address used to send expiration notifications
|
||||
- `CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL`: Account email
|
||||
- `CLOUDFLARE_DNS_API_TOKEN`: API token with DNS:Edit permission
|
||||
- `CLOUDFLARE_ZONE_API_TOKEN`: API token with Zone:Read permission
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to test your configuration first, use the Let's Encrypt staging server by uncommenting this:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#- --certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.caserver=https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If it worked, you will see the staging certificate at https://nas.domain.com.
|
||||
You may remove the `./letsencrypt/acme.json` file and restart the services to issue the real certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing from the outside
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to make it reachable from outside the network without opening ports or exposing it to the internet, I found
|
||||
[Tailscale](https://tailscale.com/) to be a great solution: create a network, run the client on both the NAS and the device
|
||||
you are connecting from, and they will see each other.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the A record should point to the IP Tailscale assigned to the NAS, eg `100.xxx.xxx.xxx`:
|
||||
```
|
||||
nas.domain.com. 1 IN A 100.xxx.xxx.xxx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://tailscale.com/kb/installation/) for installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
However, this means you will always need to be connected to Tailscale to access your NAS, even locally.
|
||||
This can be remedied by overriding the DNS entry for the NAS domain like `192.168.0.10 nas.domain.com`
|
||||
in your local DNS resolver such as Pi-Hole.
|
||||
|
||||
This way, when connected to the local network, the NAS is accessible directly from the private IP,
|
||||
and from the outside you need to connect to Tailscale first, then the NAS domain will be accessible.
|
||||
96
INSTALL.md
96
INSTALL.md
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
Any Docker-capable recent Linux box.
|
||||
I am using a fresh Ubuntu Server 22.04 on a repurposed laptop so this guide reflects it,
|
||||
but it would probably work with other distributions and different versions with a few tweaks.
|
||||
I also tested this setup on a Synology DS220+ with DSM 7.0.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pre-Docker Steps
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenSSH
|
||||
|
||||
If not done during installation, install OpenSSH server for remote connection: `sudo apt install openssh-server`
|
||||
|
||||
### Static IP
|
||||
|
||||
Set a static IP, assuming `192.168.0.10` and using Google DNS servers:
|
||||
|
||||
`sudo nano /etc//netplan/00-installer-config.yaml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
|
||||
network:
|
||||
ethernets:
|
||||
enp2s0:
|
||||
dhcp4: no
|
||||
addresses:
|
||||
- 192.168.0.10/24
|
||||
gateway4: 192.168.0.1
|
||||
nameservers:
|
||||
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
|
||||
version: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the plan:
|
||||
|
||||
`sudo netplan apply`
|
||||
|
||||
You can check the server uses the right IP with `ip a`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Laptop Specific Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
If the server is installed on a laptop, you may want to disable the suspension when the lid is closed:
|
||||
|
||||
`sudo nano /etc/systemd/logind.conf`
|
||||
|
||||
Replace:
|
||||
- `#HandleLidSwitch=suspend` by `HandleLidSwitch=ignore`
|
||||
- `#LidSwitchIgnoreInhibited=yes` by `LidSwitchIgnoreInhibited=no`
|
||||
|
||||
Then restart: `sudo service systemd-logind restart`
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Install Docker by following [these instructions](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/).
|
||||
|
||||
Then, [install Compose V2](https://docs.docker.com/compose/cli-command/#install-on-linux).
|
||||
|
||||
For a global installation (both your current user and `root` when using `sudo`),
|
||||
copy `/usr/libexec/docker/cli-plugins` rather than `$HOME/.docker/cli-plugins/docker-compose`.
|
||||
|
||||
You may then run the applications with `sudo docker compose up -d`
|
||||
|
||||
Then, to update the Sonarr/Radarr/Prowlarr/Jellyfin base paths, please run `./update-config.sh`.
|
||||
This is only needed for the first time as it will update the application's configuration files to use the proper URL.
|
||||
|
||||
## NFS Share (Optional)
|
||||
|
||||
It is now time to share the folders to other local devices using NFS, as it is easy to set up and fast.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be useful to share the media folder to a local player like Kodi or computers in the local network,
|
||||
but may not be necessary if Jellyfin is going to be used to access the media.
|
||||
|
||||
Install the NFS kernel server:
|
||||
|
||||
`sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server`
|
||||
|
||||
Then edit `/etc/exports` to configure your shares:
|
||||
|
||||
`/mnt/data/media 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0(rw,all_squash,nohide,no_subtree_check,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)`
|
||||
|
||||
This will share the `media` folder to anybody on your local network (192.168.0.x).
|
||||
I purposely left out the `sync` flag that would slow down file transfer.
|
||||
On [some devices](https://forum.kodi.tv/showthread.php?tid=343434) you may need to use the `insecure` option for the share to be available.
|
||||
|
||||
Restart the NFS server to apply the changes: `sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart`
|
||||
|
||||
On other machines, you can see the shared folder by adding the following to your `/etc/fstab`:
|
||||
|
||||
`192.168.0.10:/mnt/data/media /mnt/nas nfs ro,hard,intr,auto,_netdev 0 0`
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
- [NFS setup](https://askubuntu.com/a/7124)
|
||||
- [Hardlinks and Instant Moves (Atomic-Moves)](https://trash-guides.info/Hardlinks/Hardlinks-and-Instant-Moves/)
|
||||
355
README.md
355
README.md
@ -5,56 +5,333 @@ with some Docker containers on a vanilla Linux box. The result is an opinionated
|
||||
browsing indexers to retrieve media resources and downloading them through a Wireguard VPN with port forwarding.
|
||||
SSL certificates and remote access through Tailscale are supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirements: Any Docker-capable recent Linux box with Docker Engine and Docker Compose V2.
|
||||
I am running it in Ubuntu Server 22.04; I also tested this setup on a Synology DS220+ with DSM 7.0.
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Content
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TOC -->
|
||||
* [Docker Compose NAS](#docker-compose-nas)
|
||||
* [Table of Content](#table-of-content)
|
||||
* [Applications](#applications)
|
||||
* [Quick Start](#quick-start)
|
||||
* [Environment Variables](#environment-variables)
|
||||
* [PIA Wireguard VPN](#pia-wireguard-vpn)
|
||||
* [Sonarr & Radarr](#sonarr--radarr)
|
||||
* [File Structure](#file-structure)
|
||||
* [Download Client](#download-client)
|
||||
* [Prowlarr](#prowlarr)
|
||||
* [qBittorrent](#qbittorrent)
|
||||
* [Jellyfin](#jellyfin)
|
||||
* [Traefik and SSL Certificates](#traefik-and-ssl-certificates)
|
||||
* [Accessing from the outside with Tailscale](#accessing-from-the-outside-with-tailscale)
|
||||
* [Optional Services](#optional-services)
|
||||
* [FlareSolverr](#flaresolverr)
|
||||
* [AdGuard Home](#adguard-home)
|
||||
* [Encryption](#encryption)
|
||||
* [DHCP](#dhcp)
|
||||
* [Expose DNS Server with Tailscale](#expose-dns-server-with-tailscale)
|
||||
* [Customization](#customization)
|
||||
* [NFS Share](#nfs-share)
|
||||
* [Static IP](#static-ip)
|
||||
* [Laptop Specific Configuration](#laptop-specific-configuration)
|
||||
<!-- TOC -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The following applications are available:
|
||||
| **Application** | **Description** | **Image** | **URL** |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| [Sonarr](https://sonarr.tv) | PVR for newsgroup and bittorrent users | [linuxserver/sonarr](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/sonarr) | /sonarr |
|
||||
| [Radarr](https://radarr.video) | Movie collection manager for Usenet and BitTorrent users | [linuxserver/radarr](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/radarr) | /radarr |
|
||||
| [Prowlarr](https://github.com/Prowlarr/Prowlarr) | Indexer aggregator for Sonarr and Radarr | [linuxserver/prowlarr:develop](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/prowlarr)<br/>`develop` tag as it is not stable yet | /prowlarr |
|
||||
| [PIA Wireguard VPN](https://github.com/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia) | Encapsulate qBittorrent traffic in [PIA](https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/) using [Wireguard](https://www.wireguard.com/) with port forwarding. | [thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia](https://hub.docker.com/r/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia) | |
|
||||
| [qBittorrent](https://www.qbittorrent.org) | Bittorrent client with a complete web UI<br/>Uses VPN network<br/>Using Libtorrent 1.x | [linuxserver/qbittorrent:4.5.0-libtorrentv1](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/qbittorrent) | /qbittorrent |
|
||||
| [Jellyfin](https://jellyfin.org) | Media server designed to organize, manage, and share digital media files to networked devices | [linuxserver/jellyfin](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/jellyfin) | /jellyfin |
|
||||
| [Heimdall](https://heimdall.site) | Application dashboard | [linuxserver/heimdall](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/heimdall) | / |
|
||||
| [Traefik](https://traefik.io) | Reverse proxy | [traefik](https://hub.docker.com/_/traefik) | |
|
||||
| [Watchtower](https://containrrr.dev/watchtower/) | Automated Docker images update | [watchtower](https://hub.docker.com/r/containrrr/watchtower) | |
|
||||
| [FlareSolverr](https://github.com/FlareSolverr/FlareSolverr) | Optional- Proxy server to bypass Cloudflare protection in Prowlarr | [flaresolverr](https://hub.docker.com/r/flaresolverr/flaresolverr) | |
|
||||
| [AdGuard Home](https://adguard.com/en/adguard-home/overview.html) | Optional - Network-wide software for blocking ads & tracking | [adguardhome](https://hub.docker.com/r/adguard/adguardhome) | |
|
||||
| [DHCP Relay](https://github.com/modem7/DHCP-Relay) | Optional - Docker DHCP Relay | [dhcprelay](https://hub.docker.com/r/modem7/dhcprelay) | |
|
||||
| [Traefik Certs Dumper](https://github.com/ldez/traefik-certs-dumper) | Optional - Dump ACME data from Traefik to certificates | [traefik-certs-dumper](https://hub.docker.com/r/ldez/traefik-certs-dumper) | |
|
||||
|
||||
- [Sonarr](https://sonarr.tv/): PVR for newsgroup and bittorrent users
|
||||
- [Radarr](https://radarr.video/): Movie collection manager for Usenet and BitTorrent users
|
||||
- [Prowlarr](https://github.com/Prowlarr/Prowlarr): Indexer aggregator for Sonarr and Radarr
|
||||
- [qBittorrent](https://www.qbittorrent.org/): Bittorrent client with a complete web UI
|
||||
- [PIA Wireguard VPN](https://github.com/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia): Encapsulate qBittorrent traffic in
|
||||
[PIA](https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/) using [Wireguard](https://www.wireguard.com/) with port forwarding.
|
||||
- [Jellyfin](https://jellyfin.org/): Media server designed to organize, manage, and share digital media files to networked devices
|
||||
- [Heimdall](https://heimdall.site/): Application dashboard
|
||||
- [Traefik](https://traefik.io/): Reverse proxy
|
||||
- [Watchtower](https://containrrr.dev/watchtower/): Automated Docker images update
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
`cp .env.example .env`, edit to your needs then `sudo docker compose up -d`.
|
||||
|
||||
See [installation instructions](./INSTALL.md).
|
||||
For the first time, run `./update-config.sh` to update the applications base URLs.
|
||||
|
||||
TLDR: `cp .env.example .env`, edit to your needs then `sudo docker compose up -d`, then for the first time `./update-config.sh`.
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
| Variable | Description | Default |
|
||||
|-----------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------|
|
||||
| `COMPOSE_FILE` | Docker compose files to load | `docker-compose.yml` |
|
||||
| `COMPOSE_PATH_SEPARATOR` | Path separator between compose files to load | `:` |
|
||||
| `USER_ID` | ID of the user to use in Docker containers | `1000` |
|
||||
| `GROUP_ID` | ID of the user group to use in Docker containers | `1000` |
|
||||
| `TIMEZONE` | TimeZone used by the container. | `America/New_York` |
|
||||
| `DATA_ROOT` | Host location of the data files | `/mnt/data` |
|
||||
| `DOWNLOAD_ROOT` | Host download location for qBittorrent, should be a subfolder of `DATA_ROOT` | `/mnt/data/torrents` |
|
||||
| `PIA_LOCATION` | Servers to use for PIA | `ca` (Montreal, Canada) |
|
||||
| `PIA_USER` | PIA username | |
|
||||
| `PIA_PASS` | PIA password | |
|
||||
| `PIA_LOCAL_NETWORK` | PIA local network | `192.168.0.0/16` |
|
||||
| `HOSTNAME` | Hostname of the NAS, could be a local IP or a domain name | |
|
||||
| `ADGUARD_HOSTNAME` | AdGuard Home hostname used, if enabled | |
|
||||
| `LETS_ENCRYPT_EMAIL` | E-mail address used to send expiration notifications | |
|
||||
| `CLOUDFLARE_EMAIL` | CloudFlare Account email | |
|
||||
| `CLOUDFLARE_DNS_API_TOKEN` | API token with `DNS:Edit` permission | |
|
||||
| `CLOUDFLARE_ZONE_API_TOKEN` | API token with `Zone:Read` permission | |
|
||||
|
||||
See [configuration](./CONFIGURATION.md).
|
||||
## PIA Wireguard VPN
|
||||
|
||||
## Containers
|
||||
I chose PIA since it supports Wireguard and [port forwarding](https://github.com/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia/issues/26#issuecomment-868165281),
|
||||
but you could use other providers:
|
||||
|
||||
| **Application** | **Image** | **URL** | **Notes** |
|
||||
|-------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------|-------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Sonarr | [linuxserver/sonarr](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/sonarr) | /sonarr | |
|
||||
| Radarr | [linuxserver/radarr](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/radarr) | /radarr | |
|
||||
| Prowlarr | [linuxserver/prowlarr:develop](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/prowlarr) | /prowlarr | `develop` tag as it is not stable yet |
|
||||
| PIA Wireguard VPN | [thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia](https://hub.docker.com/r/thrnz/docker-wireguard-pia) | | |
|
||||
| qBittorrent | [linuxserver/qbittorrent:4.5.0-libtorrentv1](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/qbittorrent) | /qbittorrent | Uses VPN network<br>Using Libtorrent 1.x |
|
||||
| Jellyfin | [linuxserver/jellyfin](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/jellyfin) | /jellyfin | |
|
||||
| Heimdall | [linuxserver/heimdall](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/heimdall) | / | |
|
||||
| Traefik | [traefik](https://hub.docker.com/_/traefik) | | |
|
||||
| Watchtower | [watchtower](https://hub.docker.com/r/containrrr/watchtower) | | |
|
||||
- OpenVPN: [linuxserver/openvpn-as](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/openvpn-as)
|
||||
- Wireguard: [linuxserver/wireguard](https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/wireguard)
|
||||
- NordVPN + OpenVPN: [bubuntux/nordvpn](https://hub.docker.com/r/bubuntux/nordvpn/dockerfile)
|
||||
- NordVPN + Wireguard (NordLynx): [bubuntux/nordlynx](https://hub.docker.com/r/bubuntux/nordlynx)
|
||||
|
||||
For PIA + Wireguard, fill `.env` and fill it with your PIA credentials.
|
||||
|
||||
## Improvement
|
||||
The location of the server it will connect to is set by `LOC=ca`, defaulting to Montreal - Canada.
|
||||
|
||||
There is always room for improvement. I did not need those containers, so I did not include them, but maybe you could
|
||||
benefit from:
|
||||
## Sonarr & Radarr
|
||||
|
||||
- [Bazarr](https://www.bazarr.media/): companion application to Sonarr and Radarr that manages and downloads subtitles
|
||||
- [Lidarr](https://lidarr.audio/): music collection manager for Usenet and BitTorrent users
|
||||
- [FlareSolverr](https://github.com/FlareSolverr/FlareSolverr): Proxy server to bypass Cloudflare protection, useful
|
||||
for some indexers in Prowlarr
|
||||
- [Jackett](https://github.com/Jackett/Jackett): API Support for your favorite torrent trackers, as a Prowlarr replacement
|
||||
- [Pi-hole](https://pi-hole.net/): DNS that blocks ads
|
||||
- Expose services with CloudFlare Tunnel if Tailscale is not enough
|
||||
- you tell me!
|
||||
### File Structure
|
||||
|
||||
Sonarr and Radarr must be configured to support hardlinks, to allow instant moves and prevent using twice the storage
|
||||
(Bittorrent downloads and final file). The trick is to use a single volume shared by the Bittorrent client and the *arrs.
|
||||
Subfolders are used to separate the TV shows from the movies.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration is well explained by [this guide](https://trash-guides.info/Hardlinks/How-to-setup-for/Docker/).
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, the final structure of the shared volume will be as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
data
|
||||
├── torrents = shared folder qBittorrent downloads
|
||||
│ ├── movies = movies downloads tagged by Radarr
|
||||
│ └── tv = movies downloads tagged by Sonarr
|
||||
└── media = shared folder for Sonarr and Radarr files
|
||||
├── movies = Radarr
|
||||
└── tv = Sonarr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go to Settings > Management.
|
||||
In Sonarr, set the Root folder to `/data/media/tv`.
|
||||
In Radar, set the Root folder to `/data/media/movies`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Client
|
||||
|
||||
Then qBittorrent can be configured at Settings > Download Clients. Because all the networking for qBittorrent takes
|
||||
place in the VPN container, the hostname for qBittorrent is the hostname of the VPN container, ie `vpn`, and the port is `8080`:
|
||||
|
||||
## Prowlarr
|
||||
|
||||
The indexers are configured through Prowlarr. They synchronize automatically to Radarr and Sonarr.
|
||||
|
||||
Radarr and Sonarr may then be added via Settings > Apps. The Prowlarr server is `http://prowlarr:9696/prowlarr`, the Radarr server
|
||||
is `http://radarr:7878/radarr` and Sonarr `http://sonarr:8989/sonarr`:
|
||||
|
||||
Their API keys can be found in Settings > Security > API Key.
|
||||
|
||||
## qBittorrent
|
||||
|
||||
Set the default save path to `/data/torrents` in Settings, and restrict the network interface to Wireguard (`wg0`).
|
||||
|
||||
The web UI login page can be disabled on for the local network in Settings > Web UI > Bypass authentication for clients
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.0.0/16
|
||||
127.0.0.0/8
|
||||
172.17.0.0/16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Jellyfin
|
||||
|
||||
To enable [hardware transcoding](https://jellyfin.org/docs/general/administration/hardware-acceleration/),
|
||||
depending on your system, you may need to update the following block:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
devices:
|
||||
- /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128
|
||||
- /dev/dri/card0:/dev/dri/card0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, running Docker on Linux you will want to use VA-API, but the exact mount paths may differ depending on your
|
||||
hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
## Traefik and SSL Certificates
|
||||
|
||||
While you can use the private IP to access your NAS, how cool would it be for it to be accessible through a subdomain
|
||||
with a valid SSL certificate?
|
||||
|
||||
Traefik makes this trivial by using Let's Encrypt and one of its
|
||||
[supported ACME challenge providers](https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/acme).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's assume we are using `nas.domain.com` as custom subdomain.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea is to create an A record pointing to the private IP of the NAS, `192.168.0.10` for example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
nas.domain.com. 1 IN A 192.168.0.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The record will be publicly exposed but not resolve given this is a private IP.
|
||||
|
||||
Given the NAS is not accessible from the internet, we need to do a dnsChallenge.
|
||||
Here we will be using CloudFlare, but the mechanism will be the same for all DNS providers
|
||||
baring environment variable changes, see the Traefik documentation above and [Lego's documentation](https://go-acme.github.io/lego/dns).
|
||||
|
||||
Then, fill the CloudFlare `.env` entries.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to test your configuration first, use the Let's Encrypt staging server by uncommenting this:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#- --certificatesresolvers.myresolver.acme.caserver=https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If it worked, you will see the staging certificate at https://nas.domain.com.
|
||||
You may remove the `./letsencrypt/acme.json` file and restart the services to issue the real certificate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing from the outside with Tailscale
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to make it reachable from outside the network without opening ports or exposing it to the internet, I found
|
||||
[Tailscale](https://tailscale.com) to be a great solution: create a network, run the client on both the NAS and the device
|
||||
you are connecting from, and they will see each other.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the A record should point to the IP Tailscale assigned to the NAS, eg `100.xxx.xxx.xxx`:
|
||||
```
|
||||
nas.domain.com. 1 IN A 100.xxx.xxx.xxx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://tailscale.com/kb/installation) for installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
However, this means you will always need to be connected to Tailscale to access your NAS, even locally.
|
||||
This can be remedied by overriding the DNS entry for the NAS domain like `192.168.0.10 nas.domain.com`
|
||||
in your local DNS resolver such as Pi-Hole.
|
||||
|
||||
This way, when connected to the local network, the NAS is accessible directly from the private IP,
|
||||
and from the outside you need to connect to Tailscale first, then the NAS domain will be accessible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional Services
|
||||
|
||||
As their name would suggest, optional services are not launched by default. They have their own `docker-compose.yml` file
|
||||
in their subfolders. To enable a service, append it to the `COMPOSE_FILE` environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Say you want to enable FlareSolverr, you should have `COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:flaresolverr/docker-compose.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
### FlareSolverr
|
||||
|
||||
In Prowlarr, add the FlareSolverr indexer with the URL http://flaresolverr:8191/
|
||||
|
||||
### AdGuard Home
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `ADGUARD_HOSTNAME`, I chose a different subdomain to use secure DNS without the folder.
|
||||
|
||||
On first run, specify the port 3000 and enable listen on all interfaces to make it work with Tailscale.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Encryption
|
||||
|
||||
In Settings > Encryption Settings, set the certificates path to `/opt/adguardhome/certs/certs/<YOUR_HOSTNAME>.crt`
|
||||
and the private key to `/opt/adguardhome/certs/private/<YOUR_HOSTNAME>.key`, those files are created by Traefik cert dumper
|
||||
from the ACME certificates Traefik generates in JSON.
|
||||
|
||||
#### DHCP
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the AdGuard Home DHCP server, for example because your router does not allow changing its DNS server,
|
||||
you will need to select the `eth0` DHCP interface (or at least NOT the one that is `10.0.0.10`), then specify the
|
||||
Gateway IP to match your router address (`192.168.0.1` for example) and set a range of IP addresses assigned to local
|
||||
devices.
|
||||
|
||||
In the configuration (`adguardhome/conf/AdGuardHome.yaml`), set the DHCP options 6th key to your NAS internal IP address:
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
dhcp:
|
||||
dhcpv4:
|
||||
options:
|
||||
- 6 ips 192.168.0.10,192.168.0.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expose DNS Server with Tailscale
|
||||
|
||||
Based on [Tailscale's documentation](https://tailscale.com/kb/1114/pi-hole), it is easy to use your AdGuard server everywhere.
|
||||
Just make sure that AdGuard Home listens to all interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
## Customization
|
||||
|
||||
You can override the configuration of a services or add new services by creating a new `docker-compose.override.yml` file,
|
||||
then appending it to the `COMPOSE_FILE` environment variable: `COMPOSE_FILE=docker-compose.yml:docker-compose.override.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
[See official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/compose/extends).
|
||||
|
||||
For example, use a [different VPN provider](https://github.com/bubuntux/nordvpn):
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
version: '3.9'
|
||||
|
||||
services:
|
||||
vpn:
|
||||
image: ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordvpn
|
||||
cap_add:
|
||||
- NET_ADMIN # Required
|
||||
- NET_RAW # Required
|
||||
environment: # Review https://github.com/bubuntux/nordvpn#environment-variables
|
||||
- USER=user@email.com # Required
|
||||
- "PASS=pas$word" # Required
|
||||
- CONNECT=United_States
|
||||
- TECHNOLOGY=NordLynx
|
||||
- NETWORK=192.168.1.0/24 # So it can be accessed within the local network
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## NFS Share
|
||||
|
||||
This can be useful to share the media folder to a local player like Kodi or computers in the local network,
|
||||
but may not be necessary if Jellyfin is going to be used to access the media.
|
||||
|
||||
Install the NFS kernel server: `sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server`
|
||||
|
||||
Then edit `/etc/exports` to configure your shares:
|
||||
|
||||
`/mnt/data/media 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0(rw,all_squash,nohide,no_subtree_check,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)`
|
||||
|
||||
This will share the `media` folder to anybody on your local network (192.168.0.x).
|
||||
I purposely left out the `sync` flag that would slow down file transfer.
|
||||
On [some devices](https://forum.kodi.tv/showthread.php?tid=343434) you may need to use the `insecure`
|
||||
option for the share to be available.
|
||||
|
||||
Restart the NFS server to apply the changes: `sudo /etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart`
|
||||
|
||||
On other machines, you can see the shared folder by adding the following to your `/etc/fstab`:
|
||||
|
||||
`192.168.0.10:/mnt/data/media /mnt/nas nfs ro,hard,intr,auto,_netdev 0 0`
|
||||
|
||||
## Static IP
|
||||
|
||||
Set a static IP, assuming `192.168.0.10` and using Google DNS servers: `sudo nano /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# This is the network config written by 'subiquity'
|
||||
network:
|
||||
ethernets:
|
||||
enp2s0:
|
||||
dhcp4: no
|
||||
addresses:
|
||||
- 192.168.0.10/24
|
||||
gateway4: 192.168.0.1
|
||||
nameservers:
|
||||
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
|
||||
version: 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the plan: `sudo netplan apply`. You can check the server uses the right IP with `ip a`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Laptop Specific Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
If the server is installed on a laptop, you may want to disable the suspension when the lid is closed:
|
||||
`sudo nano /etc/systemd/logind.conf`
|
||||
|
||||
Replace:
|
||||
- `#HandleLidSwitch=suspend` by `HandleLidSwitch=ignore`
|
||||
- `#LidSwitchIgnoreInhibited=yes` by `LidSwitchIgnoreInhibited=no`
|
||||
|
||||
Then restart: `sudo service systemd-logind restart`
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,6 @@ services:
|
||||
cap_add:
|
||||
- NET_ADMIN
|
||||
network_mode: host
|
||||
mem_limit: 20m
|
||||
mem_reservation: 6m
|
||||
|
||||
adguardhome:
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user